Sanding Systems
While conditions leading to poor adhesion have been well investigated, methods for addressing the problems have not. The main adhesion enhancer used on railway networks world wide is sand. Sanding is … Continue reading
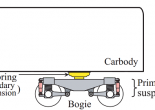
Suspension Systems for Rolling Stocks
The track irregularities and their interaction with wheel generate vibration of varying amplitude and frequency. These vibrations may cause damage to different parts of the vehicle if not contained and … Continue reading
Stray DC Current
The running rails in a DC electrified traction system are one of the main sources of electromagnetic disturbance to internal and external metallic structures and installations, such as civil works (viaducts … Continue reading
Umbrella Arch
The umbrella arch is a temporary support system forming a structural umbrella from the insertion of an assortment of longitudinal support members installed from within the tunnel, above and around … Continue reading
Railway Signalling Terms
This page will be continuously updated… Absolute Block A system of controlling rail traffic, where (under normal operations) only one train is allowed in the Block Section at a time. Proof … Continue reading
Drill and Blast Method
Drill and blast method is mostly used method for the excavation throughout the world. The method can be used in all types of rocks and the initial cost is lower … Continue reading
Ground Anchor
A prestressed grouted ground anchor is a structural element installed in soil or rock that is used to transmit an applied tensile load into the ground. Grouted ground anchors, referenced simply … Continue reading
Jet Grouting
Jet Grouting is a versatile erosion based system used to create in situ engineered geometries of soil-cement generally with limited required access. Jet Grouting creates in-situ columns of grouted soil … Continue reading
Track Circuit
Most railroads use track circuits to determine which sections of track are occupied by trains. These devices are actually fairly simple in design, and have been in use since 1872. … Continue reading
Sliding Plug Doors
A door in which the panel or panels, in the open position, are positioned parallel to and outside of the car body. Plug doors can be of the sliding plug … Continue reading
Rail-wheel Lubrication
Rail and wheel wear can be reduced dramatically by proper lubrication. In addition, lubrication can help in saving energy and reducing noise. Rail-wheel lubrications applies by automaticly or manually. Advantages of automatic lubrication; Maintenance … Continue reading
Electric Traction Systems
The system which use electrical power for traction system i.e. for railways, trams, trolleys, etc. is called electrical traction. The track electrification refers to the type of source supply system that … Continue reading
Traction Systems
A system which causes the propulsion of vehicle in which tractive or driving force is obtained from various devices such as diesel engine drives, steam engine drives, electric motors, etc. … Continue reading
Switch Heaters – Hot Air Blower
Gas, All-Electric or Oil fueled high pressure heating unit forces hot air throughout the switch area via ducts and nozzles. Complete systems designed and proven for rugged service in severe weather. Keeps switches open and … Continue reading
Axle Counter
An axle counter is a device on a railway that detects the passing of a train between two points on a track. A counting head (or detection point) is installed … Continue reading
Major Plant and Machinery for Depot Area
A. Material Handling A.1. Overhead Travelling Crane Cranes are employed for lifting and lowering materials and moving materials in a rectangular area. A.2. Jib Crane Jib crane enable lifting and lowering … Continue reading
Train Depot Area
A train depot is where trains are stabled and maintained. The depots have infrastructure to maintain the rakes with necessary facilities viz stabling lines, scheduled inspection lines, workshop for overhaul, unscheduled maintenance … Continue reading
Submerged Floating Tunnel
Tunnels in water are by no means new in civil engineering. Since about 1900, more than 100 immersed tunnels have been constructed. Bridges are the most common structures used for … Continue reading