Sanding Systems
While conditions leading to poor adhesion have been well investigated, methods for addressing the problems have not. The main adhesion enhancer used on railway networks world wide is sand. Sanding is … Continue reading
Rail-wheel Lubrication
Rail and wheel wear can be reduced dramatically by proper lubrication. In addition, lubrication can help in saving energy and reducing noise. Rail-wheel lubrications applies by automaticly or manually. Advantages of automatic lubrication; Maintenance … Continue reading
Switch Heaters – Hot Air Blower
Gas, All-Electric or Oil fueled high pressure heating unit forces hot air throughout the switch area via ducts and nozzles. Complete systems designed and proven for rugged service in severe weather. Keeps switches open and … Continue reading
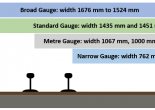
Rail Gauges
The gauge of a railway track is defined as the clear minimum perpendicular distance between the inner faces of the two rails. The different gauges can broadly be divided into … Continue reading
Buckled Rail
On warm days, rails in direct sunshine can be as much as 20 degrees centigrade above air temperature. As rails are made out of steel, they expand as they heat … Continue reading
Guard Rail
Guardrails (also known as guard/ girder/ restraining/ check rails) are used in transit systems to reduce rail wear in sharp curves and to increase the track’s resistance to flange climb … Continue reading
Flash-butt Welding
The welding process is in principle a regulated electric short circuit with the two rail ends functioning as D.C. poles. The high current produces an arc between the rail ends, … Continue reading
Structure Gauge and Kinematic Envelope
To ensure that the path required for the passage of trains is kept clear along the route of a railway, a “structure gauge” is imposed. This has the effect of … Continue reading
Turnouts
Turnouts and crossovers, including switches, frogs, guard rails, stock rails, and closure rails; rail fastening assemblies unique to turnouts; and miscellaneous components associated with turnouts, including switch rods and gauge plates. Crossover … Continue reading
Derailment
A derailment is said to take place when a vehicle (for example a train) runs off its rails. This does not necessarily mean that it leaves its track. Although many … Continue reading
Buffer Stop
A buffer stop or bumper is a device to prevent railway vehicles from going past the end of a physical section of track. The design of the buffer stop is dependent in part upon the … Continue reading
Rail Fastenings
Any device used to secure running rails into chairs or baseplates or directly to sleepers, bearers or other rail supports. Rail fastenings keeps rails fastened to sleepers (transfer of forces), … Continue reading
Rail Profile
The weight of a rail per length is an important factor in determining rails strength and hence axleloads and speeds. Weights are measured in pounds per yard or kilograms per … Continue reading
Thermit Welding
When applied to the reduction of Iron oxides, the exothermic reaction generates sufficient energy to raise the reaction product temperature to in excess of 3,000°C at which both the metal … Continue reading
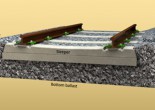
Track Structure
The track on a railway (non-US) or railroad (US), also known as the permanent way, is the structure consisting of the rails, fasteners, sleepers and ballast (or slab track), plus … Continue reading