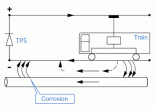
Stray DC Current
The running rails in a DC electrified traction system are one of the main sources of electromagnetic disturbance to internal and external metallic structures and installations, such as civil works (viaducts … Continue reading
Electric Traction Systems
The system which use electrical power for traction system i.e. for railways, trams, trolleys, etc. is called electrical traction. The track electrification refers to the type of source supply system that … Continue reading
Traction Systems
A system which causes the propulsion of vehicle in which tractive or driving force is obtained from various devices such as diesel engine drives, steam engine drives, electric motors, etc. … Continue reading
Energy efficiency – Replace lamps with more energy efficient ones
Since many metro and light rail stations were built in the 20th century, lighting in many stations is conventional. That means that lighting with fluorescent lighting tubes and (incandescent) light … Continue reading
Catenary Section Insulators
The section insulator (SI) is a device installed in the catenary system for electrical separation of two electrical feeds while allowing for the passage of a vehicle pantograph, such as … Continue reading
Pantograph
Pantograph is an apparatus which mounted on the roof of electric train to collect power through with an overhead tension wire. It lift or down on the basis of the … Continue reading
Rigid Catenary (or Overhead Contact System)
The rigid catenary is an Overhead Contact System (OCS) that can replace, with many advantages, the contact wire with sustentation wire, the third rail or the suspended bimetallic T-rail. It … Continue reading
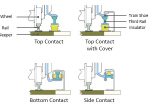
Third Rail
A third rail is a method of providing electric power to a railway train, through a continuous rigid conductor placed alongside or between the rails of a railway track. It … Continue reading