Tag Archives: track
Railway Signalling Terms
This page will be continuously updated… Absolute Block A system of controlling rail traffic, where (under normal operations) only one train is allowed in the Block Section at a time. Proof … Continue reading
Track Circuit
Most railroads use track circuits to determine which sections of track are occupied by trains. These devices are actually fairly simple in design, and have been in use since 1872. … Continue reading
Rail-wheel Lubrication
Rail and wheel wear can be reduced dramatically by proper lubrication. In addition, lubrication can help in saving energy and reducing noise. Rail-wheel lubrications applies by automaticly or manually. Advantages of automatic lubrication; Maintenance … Continue reading
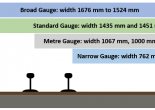
Rail Gauges
The gauge of a railway track is defined as the clear minimum perpendicular distance between the inner faces of the two rails. The different gauges can broadly be divided into … Continue reading
Buckled Rail
On warm days, rails in direct sunshine can be as much as 20 degrees centigrade above air temperature. As rails are made out of steel, they expand as they heat … Continue reading
Turnouts
Turnouts and crossovers, including switches, frogs, guard rails, stock rails, and closure rails; rail fastening assemblies unique to turnouts; and miscellaneous components associated with turnouts, including switch rods and gauge plates. Crossover … Continue reading
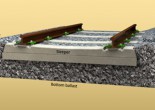
Track Structure
The track on a railway (non-US) or railroad (US), also known as the permanent way, is the structure consisting of the rails, fasteners, sleepers and ballast (or slab track), plus … Continue reading
High-speed Rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of passenger rail transport that operates significantly faster than the normal speed of rail traffic. Specific definitions by the European Union include 200 km/h … Continue reading