Buffer Stop
A buffer stop or bumper is a device to prevent railway vehicles from going past the end of a physical section of track. The design of the buffer stop is dependent in part upon the kind of couplings that the railway uses, since the coupling gear is the first part of the vehicle that the buffer stop touches.
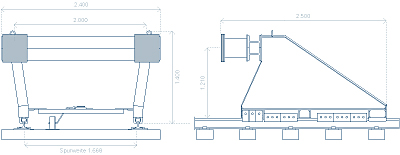
1- Friction Buffer Stops
The purpose of a friction buffer block is to secure the track end and its direct surroundings as well as the rail vehicles themselves. If the brakes fail, the buffer stop should be designed to decelerate the vehicle safely and in controlled manner until it stops.

If a single friction buffer stop is not sufficient due to the high kinetic energy of the potential impact of a vehicle, additional brakes are needed which increase the braking force in steps in case of an impact. In view of the high braking forces in such a case and to prevent damage to the track, a reinforcement of the track is required in many cases.
2- Fixed Buffer Stops
a- Fixed Buffer Stop With Hydraulic Dampers
In tracks with space only for a fixed buffer stop the buffer effect can be improved by a braking device on buffer level. The braking devices can be mechanical or hydraulic, however, their kinetic energy absorption capacity is limited. Fixed buffer stops without the possibility of kinetic energy absorption merely mark the end of the track

Fixed buffer stops with hydraulic dampers can be fastened to the track end in different ways:
- by clamps at the rail head (no drilling of rail)
- by bolting to the rail web
- by fastening to an available concrete foundation or plinth
- by fastening to an available concrete wall
Advantages over friction buffer stops include smaller footprint area and maintenance-free dampers; drawbacks are lower energy absorption capacity and higher cost.
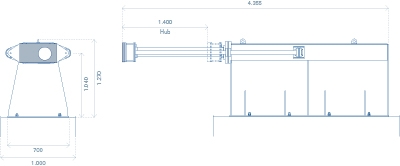
b- Fixed Buffer Stop with Mechanical Dampers
In fixed buffer stops, a mechanical buffer device absorbs the energy and converts it into friction and heat.
Advantages include little footprint space, maintenance-free operation (after an impact, this buffer stop merely needs repositioning) and lower cost; a drawback in comparison with friction buffer stops is the lower energy absorption capacity.
The following design versions are used:
- ‘Tube-in-tube’ with hydraulic cylinder
- with anti-torsion lock for positioning of the impact plate or housing
- with double shaft guide for positioning of the impact plate or housing
c- Simple Fixed Buffer Stop
The only purpose of the smple fixed buffer stop is to mark the end of track, it cannot absorb energy. It does not protect persons or the vehicle.
3- Folding / Retractable Buffer Stop Systems
For temporary blocking a track, folding buffer stops can be used – either as fixed buffer stops or with hydraulic absorbers or as conventional friction buffer stops whose braking elements can also be fastened to braking rails arranged parallel with the running track. A special design version of this buffer stop type is a retractable or sinking buffer stop.


4- Wheel Braking And Wheel Holding Systems – Wheel Locks
If a buffer stop cannot be used – e.g., on rail vehicles which have no suitable facilities at their front – braking facilities can be applied at the wheel directly.
a- Chock
To prevent a rail vehicle from rolling off, a fixed, non-braking chock is mounted or folded over the track rails.

b- Track Lock
If the primary task is that of protecting people and assets, a track section can be protected by a track lock which causes a controlled derailment of the rail vehicle.

c- Brake Shoes
Brake shoes are clamped into the track rails and linked to a brake element. If a vehicle impacts the shoe, the braking action is obtained by the incipient friction in relation to the moving mass of the rail vehicle. Brake shoes should always be applied in pairs.

Special designs are available for trams and light-weight vehicles.
Brake shoes can be attached to be folding on one or two additional rails so that they can be hinged away from the track rails.
- on central rail, inside – The braking force is distributed evenly on both wheels of the vehicle on a single central rail .
- on additional rails, outside – If no internals can be installed in the track outside brake shoes are a solution
d- Dowty Retarder
Dowty retarder is an hydraulic device that regulates the speed of rail cars as they roll down an inclined track. The devices are built for a specified speed, set at the factory. If the rail car is below the set speed, the device offers no resistance. If the car speed is at or greater than the speed setting, an internal valve is activated to provide a resistance to the wheel, thus slowing the car. This keeps cars rolling within a relatively narrow range of speeds.

Videos:
Source: rawie.de, wikipedia.com